Today, edtech platforms get regular updates, adapt new technology and features, but still struggle to retain users – about 55% of students drop out of online courses. There are several reasons behind it – lack of user engagement and the complexity of processes are of the most crucial ones. However, after the implementation of social media in elearning, edtech projects show up to 50% in overall engagement and 95% increased average attendance.
While addressing our clients’ problems, we’ve tried out various solutions for their edtech apps and the implementation of social media features in all cases demonstrated a positive impact on user motivation and retention.
Thus, in VUC^it, a personalized career coaching app, we increased user engagement by including group chats and feedback sessions with tutors, while in driving e-school Kör we implemented different user types with personal profiles and allowed drivers’ peers to be involved in the process to make it more natural and fun.
So, now let’s discuss how to integrate chats, live streams, personal profiles, and other features of social media to your apps to engage users and turn them to learning.
Messaging
Social features in edtech apps serve different purposes and one of them is providing an ability to communicate. While people send 20 billion monthly texts on Messenger only, chats can be adopted in edtech to significantly ease the learning process.
Just like social media apps, many edtech platforms come with personal and group chats. In e-learning, they take it to the next level by letting users instantly share their thoughts, files, ask questions, leave feedback, take notes, and much more.
Personal chats
Take direct 1×1 chats. In edtech apps, they enhance the learning flow by allowing fast communication between students and teachers. Tutors use direct messages to give quick feedback without interrupting other group members, while students can suggest answers, clarify information, or cooperate during or after lessons.
Apart from their main purpose, direct messages are widely used for quick multimedia sharing. This contributes to better understanding, as visuals are extremely important in education – 65% of humans are visual learners.
Additionally, personal messaging enhances privacy and allows establishing closer bonds between learners and tutors. In some e-learning platforms, shy students or those who have sensitive topics to discuss use 1×1 chats to express their concerns and ask questions that otherwise would remain unanswered.
For example, in our parenting helper app Bloss, users can directly contact the authors of helpful posts to single out the one they want to work with. That way they can directly contact experts to discuss touchy subjects like fertility, abortion, etc.
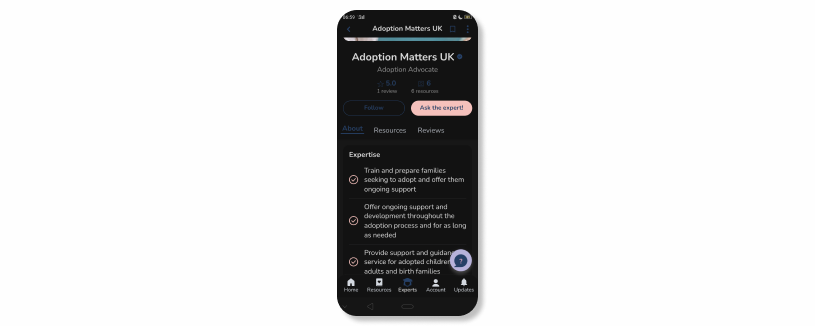
From the development perspective, social media features like 1×1 chats are not always hard to implement, as there are plenty of tools and platforms to help with it. For example, lots of edtech apps prefer Messenger which can be added to a web platform with the help of a Facebook plugin. Similarly, edtech platforms can use other apps for messaging.
Let’s take WhatsApp – we connected VUC^it user base with WhatsApp so that tutors and bots can send users encouraging texts, links to additional content, etc.
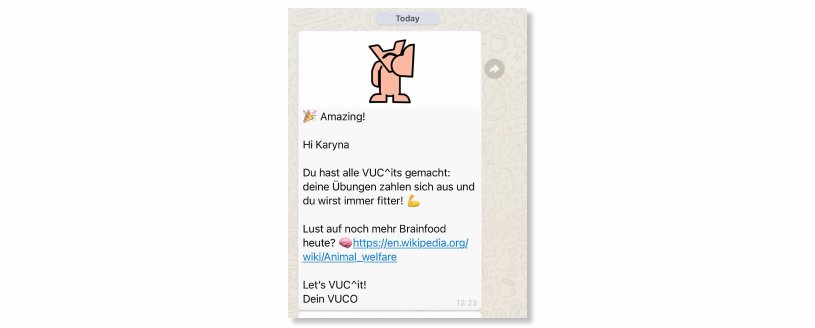
Group chats, in turn, enhance communication and collaboration between multiple users to save their time. Apart from it, edtech creators use them to share information with all students at once, hold group video lessons with Q&A sessions, start discussions, and just to share some educational stuff with each other. Their influence in edtech is just impressive – group chats can establish a meaningful online participation that speeds up the learning process in almost 75% of cases.
We also turned this to the advantage of the same VUC^it users, when designing a community section where they can find answers and chat with other team members connected through tasks & challenges.
Live streaming
Online live classes is another social media feature that has been rocking in edtech ever since the pandemic began – 62% of educators find classes with live streams more effective. This learning format is beneficial in several ways. For users, it boosts engagement and saves time, for tutors, live streaming allows to get creative and approach different user needs at once, and for companies, it is a great source of attracting new customers.
Live streams are of the most efficient social features in elearning because they are often enhanced with additional technology like digital whiteboards, screen sharing, and more. They allow users to view and replicate the tutors’ approach, which contributes to a better understanding.
Recording live sessions is a common practice too. It helps to organize students and unload tutors – learners can return to any class and experience the lesson again to find their answers, and teachers don’t have to repeat the same over and over again.
Additionally, many e-learning apps boost user involvement by reinforcing their live sessions with interactive buttons. Thus, in VUC^it, we used a “thumb up” and “like” buttons to diversify and slightly gamify the lessons. As a result, this implementation boosted user motivation, engagement, and average daily time spent in the app.

Personal profiles
One of the key social features in edutech apps is personal profiles. Implementing them in edtech is a great way to enhance personalization and customization. Here, personal accounts serve multiple purposes – from informing learning buddies about your hobbies to providing extra credibility when offering materials and services.
Let’s take a look at the Expert flow in Bloss, an education parenting platform we’ve recently developed. On the platform, experts can manage their profile pictures, credentials, and add their social media accounts. This feature helps users see “real humans” behind tutors. It also allows teachers to strengthen their credibility by posting expert content that users can review and share. The more users interact with the content, and the more positive feedback they leave, the more credibility experts get.
For Kör, our team included customized user profiles to let instructors select a personalized driving program best tailored to certain needs and skills. As a result, tutors can adjust the learning process to meet users expectations. Some might want to attend lessons only on Tuesdays, and others seek as much driving practice as possible – in all cases, detailed personal profiles help to set things up the right way.
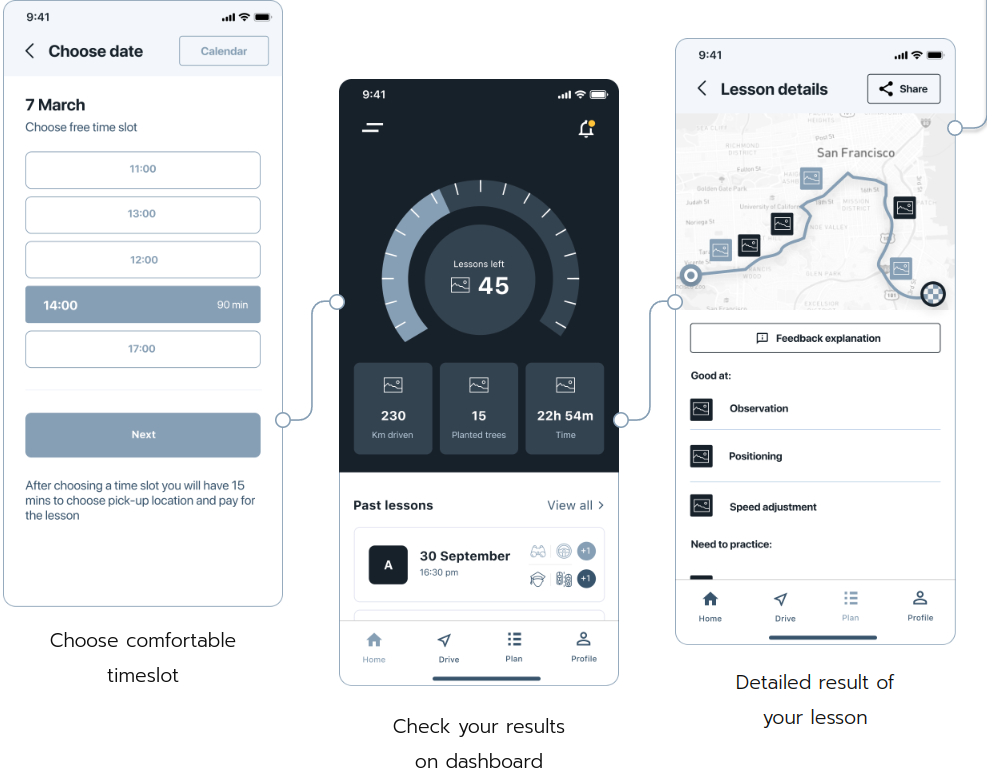
Feed
Profiles are also essential for creating a personalized feed – one of the crucial social features in edtech apps. It keeps learners updated on their preferences and enhances the sense of community. Being able to interact with other users’ content turn students to learning and drives a healthy competition.
As an example, in Bloss, we’ve added a For me section that includes popular content as well as automatically suggested posts that are offered to users based on the interests and activities listed in their profiles.
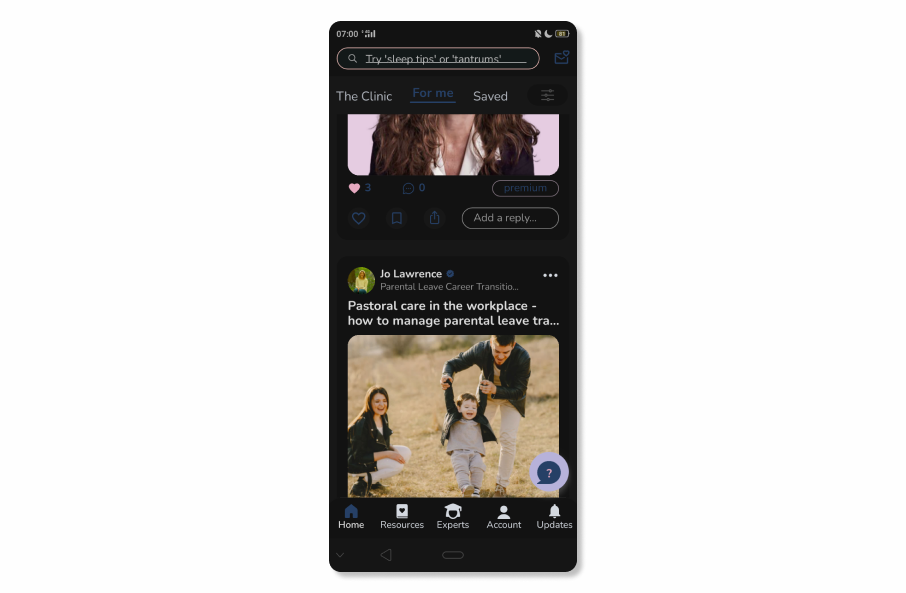
Real-Time Notifications
Online learning is often less structured as compared to traditional classes, so it can be sometimes challenging and confusing for students. However, notifications can help them out with keeping track of all important updates like new tasks, lessons, answers in discussions, uploads by tutors, etc.
Aside from the classroom reminders, notifications keep users updated on what’s happening in their groups and keep track of the upcoming events. This enhances the sense of community and contributes to user engagement.
Notifications are also linked to gamification and so-called “dopamine traps” that developers apply to motivate users to come back for more. A common practice in edtech is adding a character that “talks” to students via notifications. That is the case with Duolingo – the character named Duo reminds users to open the app and continue studying with the help of various cheering pop-ups.

Hashtags and categories
Hashtags and categories are a must-have if you’re aiming towards a comprehensive user-centered e-learning app. Edtech developers use these social media features in edtech to help users access, structure, and share information. Their efficiency is unquestionable – only in higher education instances, more than 90% of students demonstrate a positive attitude towards the use of these features.
To make navigation in our apps smooth, we usually add filters by categories and hashtags. For example, in an app like Bloss, we offer users to filter out content by 9 main categories that are further divided into smaller sections (e.g. Category: pregnancy, subcategory: morning sickness). This way, customers can easily find, access, and save content, as well as contact the author for further expertise.
Comments, likes, and reactions
Comments, quick reactions, and likes are the go to social features in e-learning. First and foremost, they are the best tools for boosting user engagement – customers get dopamine spikes whenever somebody reacts to their comments or posts with likes and reactions. This way, users become empowered, involved, and motivated to study.
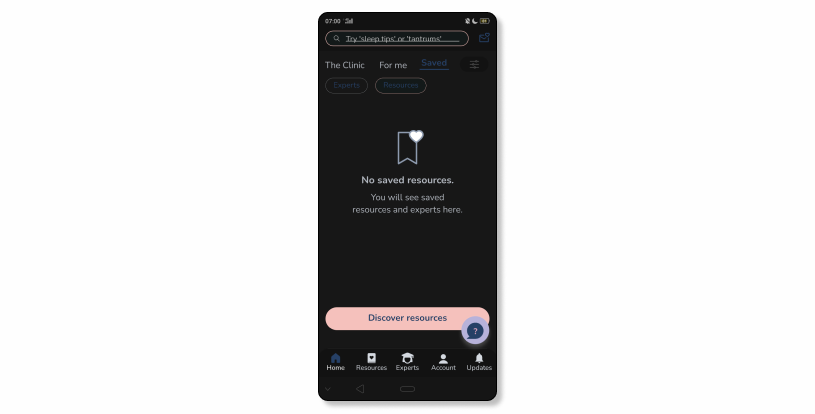
These features are also widely used in edtech to let users store and easily manage information. Typically, e-learning apps allow saving content so that users can access it later in a separate section. Take our case – in Bloss, the team has made it possible by adding the Saved tab. Just like posts in user feed, saved content can be liked, shared, and commented on.
Wrap up
Today, social media in elearning is widely applied in edtech to ease the learning process and engage users by enabling effortless communication. Additionally, social media implementations including feed, likes and comments, and notifications allow easily storing, accessing, and sharing information, which enhances the learning process and contributes to better user experience.
However, every feature has to be used properly to achieve the best results. For instance, implementing personal chats allow shy students to express their concerns, but would be inefficient as a main tool of communication during interactive group courses.